Just How Good is Generative Artificial Intelligence in Helping with Proposals?

This article was originally published February 14, 2024 on WashingtonTechnology.com
We hear a lot of hype about how generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is going to transform proposal development, but just how useful is it? Lohfeld Consulting Group recently completed a study, Benchmarking Generative AI Tools for Proposal Development, that assesses and compares the performance of public and private platforms in performing fundamental proposal tasks. This study shows that these tools have enormous capabilities but also vary widely in performance.
Key Findings
We characterized five public GenAI platforms (OpenAI’s ChatGPT-3.5, Anthropic’s Claude Instant and Claude-2-100k, Meta’s Llama-2-70b, and Google Bard) and two private, government contracting (GovCon) domain-aware GenAI platforms on eight different proposal assistance tasks. Here are some things we learned.
- Comparing the Platforms. We were pleased to see that both private platforms specifically designed for GovCon performed as well or better than the public GenAI systems. That is reassuring because, unlike many public platforms, these private platforms do not record your data for training of future models and other purposes. The architecture of these private platforms is also specifically designed to protect your data from corruption and leakage.
- Consistent Meaning. When we ran the same scenario for the same platform multiple times, we found that the underlying meaning of the responses did not change very much. GenAI platforms are designed to be creative in formatting and word use, but we were reassured to see that the impulse for creativity did not quickly drive the GenAI platforms to make things up (aka hallucinate).
- Platform Stability. We sometimes saw the public platforms unable to respond to a prompt, either hanging incomplete or answering with “unable to respond to a prompt of this length.” We found instances where a partial response could be completed simply by typing “continue” into the prompt window.
- Adaptability to Your Best Practices. With two exceptions, the GenAI chatbots were consistently able to respond to all of our engineered prompts. That will be key when it becomes time to adapt your in-house GenAI platform to your company’s best practices and knowledge management repository. The exceptions were Google Bard and Meta’s Llama-2-70b, both of which were unable to respond to prompts in more than one of the eight test scenarios.
Overview of the Study
Here is an overview of the study itself. We set the primary objectives of the study to be:
- Assess and compare the capabilities of public and private GenAI platforms to perform tasks typical of proposal development for government solicitations.
- Pinpoint specific areas where these GenAI tools exceed or fall short of expectations in proposal development tasks and characterize the implications.
We selected five public platforms (OpenAI’s ChatGPT-3.5, Google Bard, Anthropic’s Claude Instant and Claude-2-100K, Llama-2-70b) and two private platforms to be characterized.
We identified eight typical proposal tasks where, a priori, we felt that GenAI tools offer the potential increase employee productivity significantly. The eight proposal assistance tasks were:
- Idea Generation
- Drafting Proposal Narrative
- Data Analysis and Integration
- Compliance Checking
- Language and Tone Optimization
- Revision and Editing Suggestion
- Question Answering and Clarification
- Formatting and Presentation
For each proposal assistance task, we prepared a prompt that included a scenario and a tasker (called a “request”) that mirrors real-life challenges in proposal development. We also developed and applied benchmarks so we could assess each GenAI platform’s practical utility. The test methodology is shown in Figure 1.
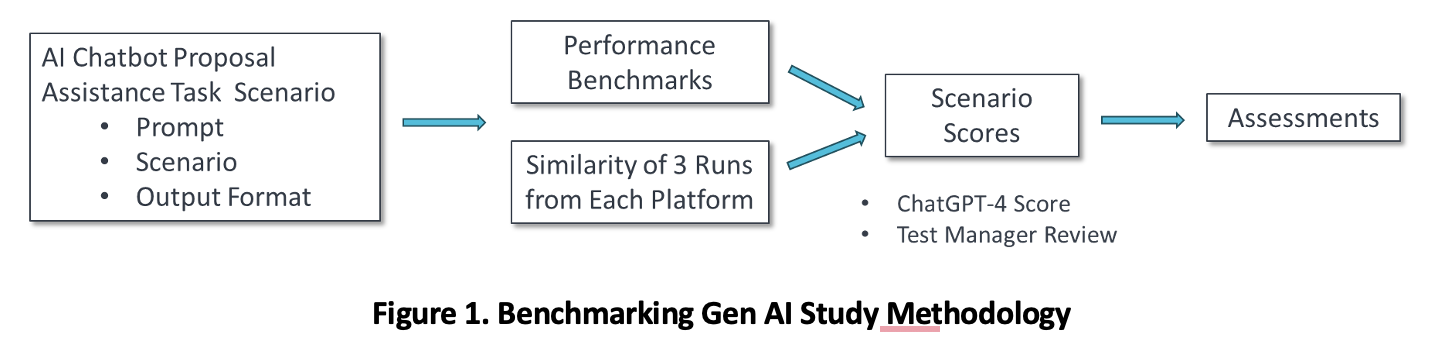
We ran each prompt three times for each platform, for a total of 168 runs (7 platforms x 8 proposal assistance tasks x 3 runs/task). For each proposal assistance task, we established benchmarks scored on an integer scale of 1 – 5. We used ChatGPT-4 to score the results, with review by a human Test Manager. We only saw one instance where the human Test Manager assessment differed from the ChatGPT-4 score by a value greater than one.
We chose not to try to characterize the performance of proposal tasks that would rely on semantic search and other techniques to give a GenAI platform secured access to data in a user’s private library for the following reasons: (1) many public platforms don’t offer this feature; (2) we would have had to create, upload, and transform such a library in each platform; and (3) our research suggested there would be major challenges in controlling variables.
Summary of Test Scenarios and Responses
The study effort generated a few surprises, a lot of reassurance, and some unexpected insights into the importance of writing good prompts. Here are some of the findings from our testing against each of the proposal assistance tasks.
- Idea Generation. Each GenAI platform was tasked to generate 20 innovative ideas responsive to one of four typical evaluation criteria (flexibility, scalability, feasibility, security) for an IT system and explain the benefit of each idea. We scored each idea on a scale of 1 – 5 for its associated evaluation criterion and for innovation. We saw the percentage of ideas generating the highest score of 5 ranging from 0% to 50%, a surprisingly wide variation. We suspect this scenario is the most sensitive to the training data for the GenAI platform. ChatGPT-3.5 and one of the private platforms realized the highest scores.
- Drafting Proposal Narrative. We tasked each GenAI platform to review a proposal for an energy project and create an executive summary with specific guidelines (e.g., state the project objectives). The benchmarks for this proposal assistance task were Compliance with Writing Guidelines and an industry-standard readability measure called Flesch-Kincaid reading ease and grade level. We note that all responses scored a Very Difficult readability on the Flesch-Kincaid assessments. Both private platforms outscored all the public platforms, and both Google Bard and Llama-2-70b failed to generate responsive outputs for the exercise. We observed that the readability of the GenAI responses was comparable to the readability of the prompt itself, but we have not yet tested to explore whether the prompt cued the readability of the GenAI responses.
- Data Integration and Analysis. We provided each GenAI platform with a proposal that included a complex dataset (related to urban traffic management) and tasked each platform to assess the significance of the dataset and write an analysis paragraph for the proposal narrative. The results for all the runs of all the platforms scored a 4 on a scale of 1 – 5, suggesting that the problem wasn’t challenging enough to see variation in responses. We were pleased to note that, despite the recognized shortcomings of GenAI platforms when it comes to arithmetic, all the platforms were able to work with statistical data.
- Compliance Checking. We tasked the GenAI platforms to review a solicitation and corresponding proposal to confirm:
- The proposal addresses all the specific project requirements, deliverables, and scope as outlined in the solicitation;
- The proposal aligns with Format and Submission Guidelines in the solicitation;
- The proposal demonstrates how it meets each evaluation criterion; and
- The proposal includes all mandatory documentation and certifications.
We were pleased to note that all GenAI platforms were able to meet this standard. In several cases, the GenAI platforms offered suggestions for improving the responses, partially addressing questions of responsiveness as well.
- Language and Tone Optimization. We gave the GenAI platforms a technical narrative and tasked them to provide a revised version “suitable for a general audience while maintaining technical accuracy.” This task is an exemplar for revising a proposal to establish a voice suitable for expected evaluators. All the GenAI platforms were able to create revisions that met or exceeded the benchmarks for Improvement in Readability and Tone and Customization for a Targeted Audience. Consistently low results (typically, 2 on a scale of 1 – 5) for the Adherence to Formal/Professional Language Standards benchmark revealed a weakness in the prompt not providing a clear definition of “general audience.” This is a valuable reminder that you need to prompt GenAI chatbots with clear instructions on audience type.
- Revision and Editing Suggestions.The GenAI platforms reviewed a narrative to provide editing suggestions to improve coherence, clarity, and persuasiveness. This emulates the role of a reviewer who is to provide suggestions specifically to improve the quality of the narrative. The results showed the greatest variability in responses of all the proposal assistance tasks; the benchmark scores ranged from 2 – 5 on a scale of 1 – 5. Claude Instant and one of the private platforms produced the highest consistent results. Interestingly, Llama-2-70b’s three runs yielded results of 5, 3, and incomplete (hung). This variability suggests that care needs to be taken to craft prompts specific to the platform and perhaps the topic. The variability also reinforces the importance of human review of results rather than just blanket acceptance of the GenAI output.
- Question Answering and Clarification. We asked the GenAI platforms to respond accurately and comprehensively to 12 complex questions for a proposal to use AI as an aid in wildlife conservation. We noted with interest that each GenAI platform was consistent in its responses for all three runs: the Claude-2-100K and Llama-2-70b platforms scored 5 every run against both benchmarks; the Bard platform hung and was unable to respond on any of its runs; and the other platforms scored 4 for every run against both benchmarks.
- Formatting and Presentation. We tasked the GenAI platforms to reformat a proposal draft according to specific guidelines, focusing on layout, readability, and professional presentation standards. The benchmarks for this task were Adherence to Specified Formatting Guidelines and Aesthetic Appeal and Professionalism of Layout. We observed significant variability in the scores, with one of the private platforms receiving the highest average score and Bard receiving the lowest score. Notably, ChatGPT-4 limited its score for the latter benchmark because it had no information on the use of color and other aesthetic tools, a reasonable caveat.
So, What Does It All Mean?
Overall, the study reinforces the idea that GenAI is going to dramatically change how businesses approach proposal writing, but in our opinion, you will only succeed by blending AI efficiency with human expertise. The GenAI chatbots we assessed have the flexibility to be adapted to your company’s best practices, but you will need to invest the time and effort to create and test the prompts that make your people more productive.
By Bruce Feldman, Managing Director, Lohfeld Consulting Group
Bruce Feldman is a Managing Director leading Lohfeld Consulting’s AI initiative and brings 30+ years of business development, capture management, and proposal development expertise specializing in Space and National Intelligence programs for the U.S. Air Force (USAF), U.S. Space Force (USSF), Intelligence Community (IC), Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD), Department of Defense (DOD) 4th Estate, and Combatant Commands. He is a retired Lt. Col., USAFR and has a MSEE from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, a BSEE from the Air Force Institute of Technology, and a BA in Chemistry from Yale University.
Lohfeld Consulting Group has proven results specializing in helping companies create winning captures and proposals. As the premier capture and proposal services consulting firm focused exclusively on government markets, we provide expert assistance to government contractors in Capture Planning and Strategy, Proposal Management and Writing, Capture and Proposal Process and Infrastructure, and Training. In the last 3 years, we’ve supported over 550 proposals winning more than $170B for our clients—including the Top 10 government contractors. Lohfeld Consulting Group is your “go-to” capture and proposal source! Start winning by contacting us at www.lohfeldconsulting.com and join us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and YouTube(TM) .
Paperback or Kindle
10 steps to creating high-scoring proposals
by Bob Lohfeld
contributors Edited by Beth Wingate
Subscribe to our free ebrief
Teaming friends, frenemies, and enemies—12 tips to mitigate harmful effects
Did you know that contracting officers spend up to 20% of their time mitigating disputes between teaming partners? In an informal poll we conducted on LinkedIn last month, 40% of respondents classified their teaming partners as “frenemies” on their last bid.
Explore Further
- Advice (542)
- AI (33)
- APMP (18)
- Army MAPS Contracts (4)
- Business Development (305)
- Capture Management (276)
- Complex Technology Grants Services (26)
- Favorite Books (5)
- GenAI (6)
- Go-to-Market (28)
- Graphics (5)
- Lohfeld Books (2)
- NASA SEWP VI Contracts (2)
- Navy SeaPort-NxG Contracts (2)
- NIST MSE Grants (1)
- NIST NAPMP Grants (2)
- Past Performance (63)
- Post-submission Phase (14)
- Pre-RFP Preparation (273)
- Proposal Management (351)
- Proposal Production (81)
- Proposal Reviews (46)
- Proposal Writing (116)
- Pursuit Phase (112)
- Research Report (4)
- Resources (64)
- Tools & Tips (437)
- Training (13)
- Uncategorized (223)

Sign Up for INSIGHTS and Download your FREE book
We'd love to help you with your proposals. Enjoy our complimentary Lohfeld Consulting Group Capture & Proposal Insights & Tips book with your FREE subscription to our Insights Newsletter.
GET YOUR FREE BOOK



